The acrosome is a structure of the spermatozoa located in the anterior part of the head, which plays a fundamental role in fertilization, as it contains enzymes necessary to penetrate the egg cell.
Alterations in the acrosome morphology are related to physiological processes due to the aging of the sperm cell. These changes in the acrosome are also related to thermal shock, cold shock, and the presence of toxins and/or micro-organisms in the medium or by repeated dilutions, washings, and centrifugations.
The acrosome is essential for fertilisation
To count a spermatozoon as normal, the following values must be taken into account:
- Normal values: >80% intact acrosomes
- Cut-off value: 60%.
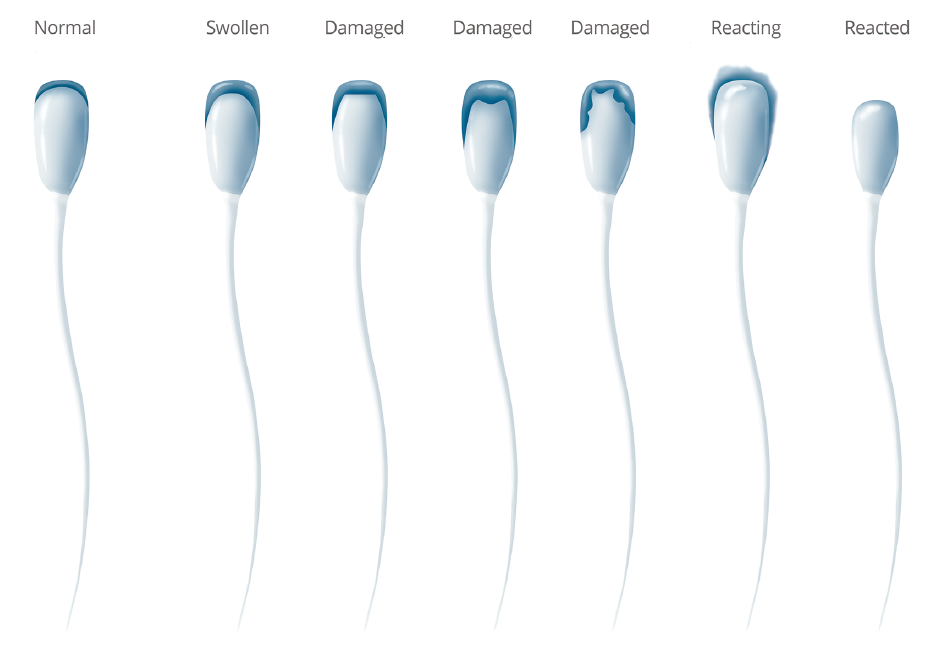
The acrosome contains enzymes that digest the oocyte coatings, allowing fertilization. Therefore, only spermatozoa with an intact acrosome are potentially fertilizing. This implies that many spermatozoa with a damaged acrosome will significantly decrease reproductive success.




